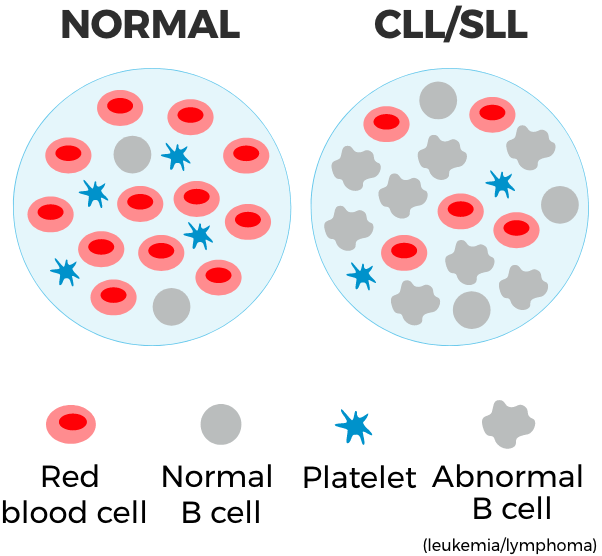
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) recommends zanubrutinib (BRUKINSA®) as a preferred treatment option for people with CLL/SLL who have or haven’t been treated before and with or without certain genetic mutations, known as del(17p) or TP53 mutations*
NCCN is a not-for-profit alliance of 33 leading cancer centers in the United States devoted to patient care, research, and education. The organization creates cancer guidelines that are considered the standard to guide treatment decisions.
* Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma V.1.2026. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2025. All rights reserved. Accessed October 10, 2025. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.